Aristaeus
A-List Customer
- Messages
- 407
- Location
- Pensacola FL
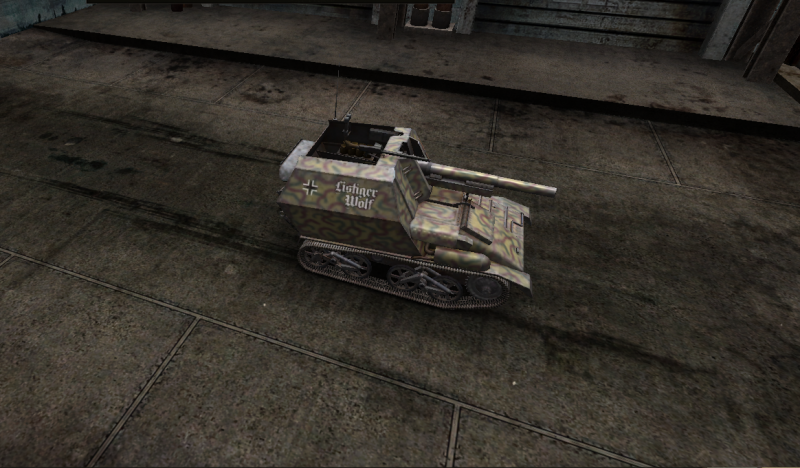
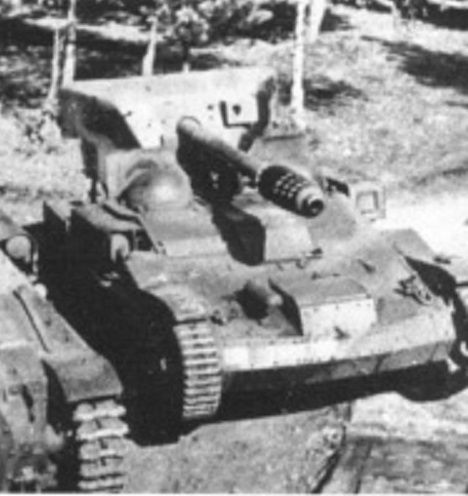
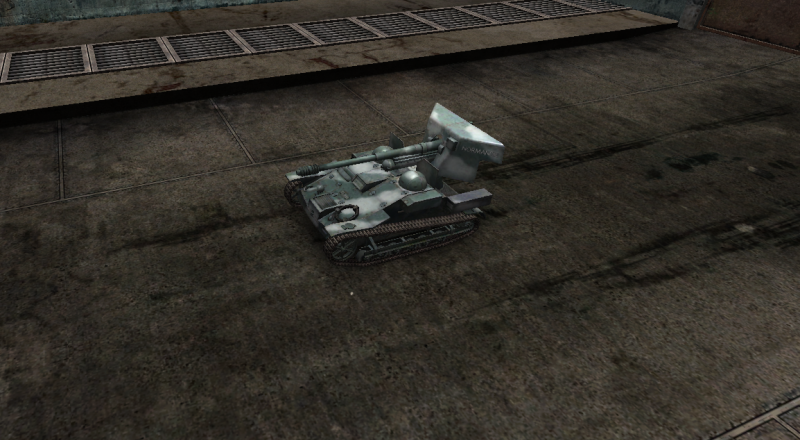
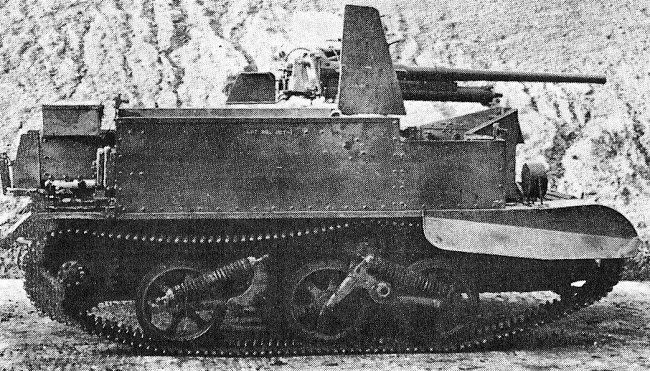
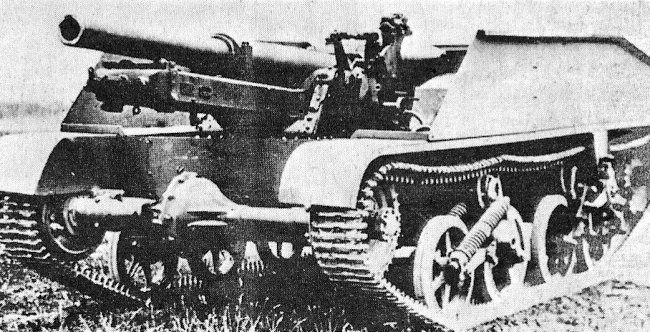
For the United States the T-18 Tank Destroyer.
Development of this self-propelled gun on the chassis of the M3 light tank started in October 1941. The first prototype passed trials in the spring of 1942, but the vehicle never saw mass production.
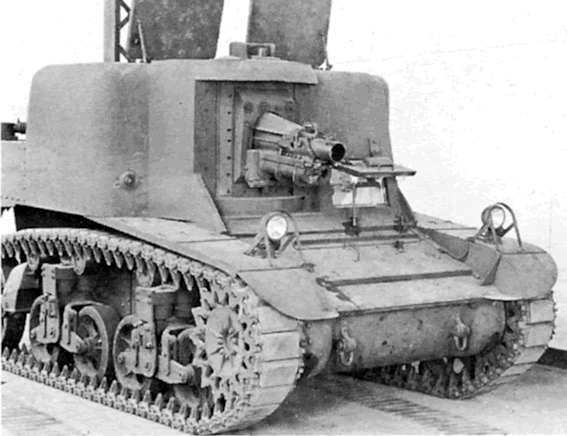
Crew:
3
Armament:
75MM Howitzer M1A1
Engine:
Continental R-975 C-1, 350HP
Chaissis:
M3
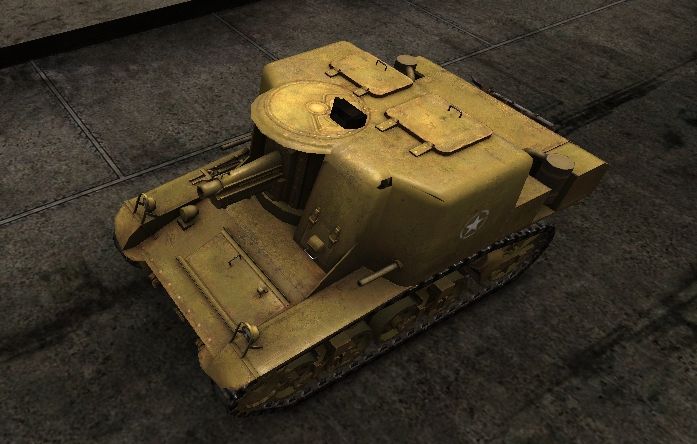

Development of this self-propelled gun on the chassis of the M3 light tank started in October 1941. The first prototype passed trials in the spring of 1942, but the vehicle never saw mass production.

Crew:
3
Armament:
75MM Howitzer M1A1
Engine:
Continental R-975 C-1, 350HP
Chaissis:
M3